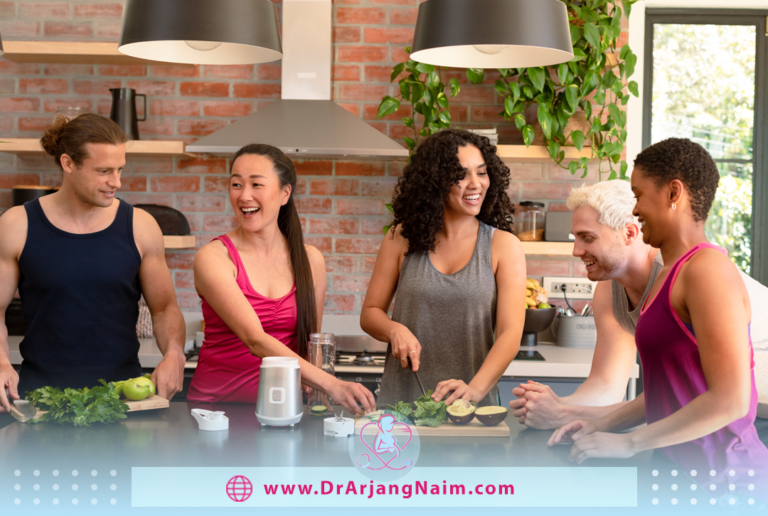
Reproductive health is a vital aspect of overall well-being and is influenced by numerous lifestyle factors. From diet and exercise to stress management and substance use, our daily choices play a significant role in fertility, menstrual health, pregnancy outcomes, and overall reproductive function. Understanding these lifestyle influences can help individuals make informed decisions that enhance their reproductive health and overall quality of life.
Diet and nutrition
A balanced diet supports hormone production, egg and sperm quality, and reproductive function. Some key nutrients that are beneficial for reproductive health include:
- Folic acid: Essential for fetal development and preventing congenital disabilities.
- Iron: Important for preventing anemia, which can affect ovulation.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish and nuts, improve blood flow to the reproductive organs.
- Zinc and selenium: Support sperm production and overall reproductive function.
- Vitamin D: Plays a role in regulating hormones and fertility.
Foods to avoid for optimal fertility
When trying to conceive, diet is important in maintaining hormonal balance, supporting ovulation, and improving overall reproductive health. Certain foods and eating habits can negatively impact fertility by increasing inflammation, disrupting hormone levels, or reducing egg and sperm quality.
Processed foods and trans fats
Highly processed foods, such as packaged snacks, fast food, and fried items, often contain trans fats and refined carbohydrates. These can contribute to insulin resistance, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances, negatively impacting fertility.
Sugary drinks and added sugar
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and increased inflammation, which can interfere with ovulation and egg quality. Excessive sugar consumption may also contribute to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a leading cause of infertility.

Too much caffeine
While moderate caffeine consumption (less than 200 mg per day) is generally considered safe, excessive consumption may increase the risk of miscarriage and fertility problems. Caffeine can also interfere with iron absorption, a mineral important for reproductive health.
Alcohol
Regular alcohol consumption can interfere with estrogen and progesterone levels, disrupt ovulation, and reduce sperm quality. Heavy alcohol consumption is linked to a higher risk of miscarriage and difficulty getting pregnant.

Physical activity and its impact
Regular physical activity improves circulation, hormone regulation, and overall reproductive function. It reduces the risk of conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and erectile dysfunction.
However, excessive high-intensity exercise, especially among women, can lead to menstrual irregularities, disrupted ovulation, and lower estrogen levels, potentially affecting fertility. Best exercises for reproductive health:
- Yoga and Pilates
- Walking and moderate cardio
- Strength training
- Maintaining a healthy weight

Maintaining a healthy weight
It is essential for reproductive health, as both obesity and being underweight can negatively impact fertility. Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and infertility while also raising estrogen levels, which may disrupt ovulation and contribute to complications like gestational diabetes and preeclampsia during pregnancy. On the other hand, being underweight can cause irregular menstrual cycles and anovulation (lack of ovulation) due to inadequate body fat, which affects estrogen production and overall fertility. Achieving a balanced weight through a nutritious diet and regular exercise can help support hormonal balance and improve the chances of conception.
Stress and mental health
Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance by elevating cortisol levels and interfering with key reproductive hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. This imbalance may lead to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation issues and, in men, contribute to erectile dysfunction and reduced sperm quality. Additionally, high-stress levels increase the risk of pregnancy complications, including preterm birth. Managing stress through mindfulness and meditation can help regulate stress hormones, while adequate sleep supports overall hormonal balance and well-being. Therapy and counseling can also be beneficial for coping with anxiety and emotional stress related to fertility challenges, promoting better reproductive health.
Sleep patterns and their role
Poor sleep quality and irregular sleep patterns can negatively impact reproductive health by disrupting hormone regulation. This can lead to altered melatonin levels, which play a role in protecting eggs from oxidative stress. Sleep deprivation can also interfere with the production of key reproductive hormones like estrogen and testosterone, potentially causing menstrual irregularities and reduced sperm quality. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, limiting screen time before bed, and practicing good sleep hygiene can help support hormonal balance and improve fertility.

Smoking
Smoking has a detrimental impact on reproductive health, as it reduces ovarian reserve, accelerates ovarian aging, and can lead to earlier menopause. In men, smoking lowers sperm count, reduces motility, and damages sperm DNA integrity, which can contribute to infertility. Additionally, smoking increases the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy, making it crucial for individuals trying to conceive to quit smoking to improve their fertility and overall reproductive outcomes.
Substance use
Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt menstrual cycles and lower fertility in women, while in men, it reduces testosterone levels and negatively affects sperm production. Similarly, recreational drugs can impair reproductive health—marijuana has been linked to lower sperm count and ovulation disorders, while cocaine and opioids can disrupt hormone production and sexual function. Quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and avoiding recreational drugs can significantly improve fertility and overall reproductive health outcomes.
Environmental and occupational hazards
Exposure to environmental toxins and occupational hazards can significantly impair reproductive health. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), commonly found in plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics, can interfere with hormone balance. At the same time, heavy metals like lead and mercury are linked to reproductive toxicity and fertility issues. Radiation and prolonged heat exposure can negatively impact sperm quality and egg viability. To reduce exposure, it’s important to use BPA-free products, choose organic foods to minimize pesticide contact, and wear protective gear in hazardous work environments, which can help safeguard reproductive health.
Sexual health and safe practices
Practicing safe sex is crucial for maintaining sexual health and preventing sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can impact reproductive well-being. Infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HPV can lead to serious complications, including infertility, if left untreated. Regular screenings allow for early detection and treatment, reducing the risk of long-term health issues. Additionally, vaccinations, such as the HPV vaccine, protect against specific infections, further promoting sexual health. Using barrier methods like condoms and maintaining open communication with partners about sexual history also play key roles in preventing STIs.
Regular gynecological and urological check-ups
Routine medical check-ups help detect and treat reproductive health issues early. For women, Pap smears and pelvic exams are important, while men should have regular screenings for testicular health and prostate function.
Dr. Arjang naim is one of the top obstetricians and gynecologists in Los Angeles, providing exceptional patient care and expertise.
Conclusion
Lifestyle choices significantly impact reproductive health, influencing fertility, pregnancy outcomes, and overall reproductive function. Individuals can enhance their reproductive well-being by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising in moderation, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding harmful substances. Regular medical check-ups, safe sexual practices, and environmental awareness further contribute to optimal reproductive health. Making informed lifestyle choices improves fertility and enhances overall health and quality of life.
Additional questions
- Can lifestyle changes improve fertility?
For both women and men, the keys to fertility include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, and choosing foods that support your ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. Thirty percent of infertility is related to weight gain. Infertility rates are 3 times higher in obese women.
- What damages egg quality?
Egg quality can be affected by factors like age, smoking, excessive alcohol, poor diet, obesity, and stress. Medical conditions such as PCOS or endometriosis, as well as treatments like chemotherapy, can also impair egg health. Environmental toxins and genetics may contribute, highlighting the importance of a healthy lifestyle and medical guidance.
- How does smoking affect fertility in women?
Smoking significantly increases the likelihood of infertility in women, with studies showing that smoking women are more likely to experience infertility compared to nonsmoking women. Smoking may also accelerate the onset of menopause by 1 to 4 years. Additionally, smoking is linked to a higher risk of miscarriage in both natural and assisted reproductive technology (ART) pregnancies.
- Why does cancer cause infertility?
Some cancer treatments affect the number of eggs in the ovaries. This is called ovarian reserve. Low ovarian reserve may mean that there is less time to get pregnant. Menopause may come earlier because of the treatment you have had.
- Can drinking water improve egg quality?
Drinking water is essential for overall health, including reproductive health, but it does not directly improve egg quality. Staying hydrated supports the body’s natural functions, including hormone regulation and maintaining cervical mucus, which can help with fertility. However, while hydration is important, egg quality is directly affected by age, genetics, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions. Drinking water can help create a healthy environment for your reproductive tract, but it alone is not a guaranteed way to improve egg quality.
References
https://westmeadfertilitycentre.com.au/how-healthy-lifestyle-choices-can-improve-your-fertility/
https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/weight-loss-and-sleep