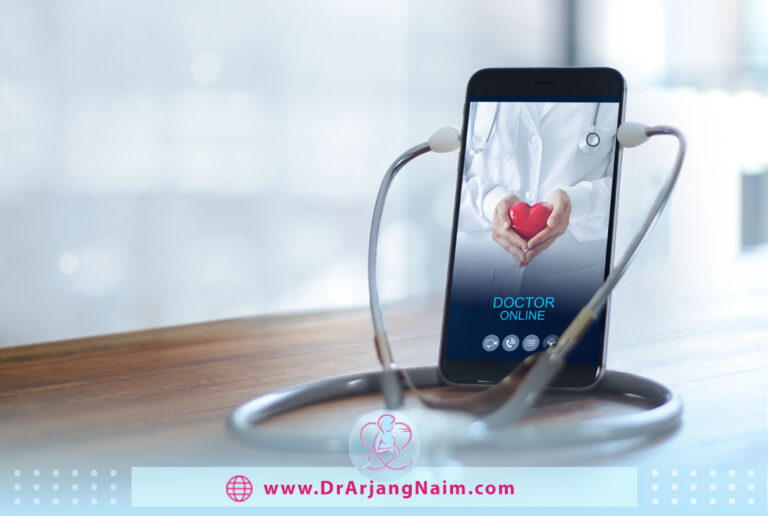
Telemedicine is exchanging medical information from one place to another using electronic communication that improves the patient’s health status. Telemedicine has many uses and can be used for various services, including wireless devices, email, two-way video, smartphones, and other methods of telecommunication technology.
Beginning more than 40 years ago with the expansion of hospital services to patients in remote locations, telemedicine has rapidly become part of specialty departments, hospitals, private physician offices, home health care, and the workplace.
History of telemedicine
Contrary to popular belief, telemedicine is a method that has been used previously. The concept of telemedicine dates back to the 19th century. What started with a few hospitals wanting to reach patients in remote locations has evolved into an integrated system across the care chain. The history of telemedicine will show how we got to where we are today.
Telemedicine in the 19th century
The creation of telemedicine began with telecommunication infrastructure, which included the telegraph, telephone, and radio. Casualties and injuries were reported using the telegraph, ordering medical supplies and advice during the Civil War. It is considered one of the first adoptions of telemedicine technology.
Telemedicine in the 20th century
In 1922, Dr. Hugo Gernsback demonstrated teledactyl in a scientific journal. Gernsback predicted this sensory feedback device would allow doctors to see patients through a television screen and touch them from miles away with robotic arms.
The first radiological images were sent by telephone between two medical staff at two different health centers in Pennsylvania in 1948. Health centers were 24 miles apart! Then in 1959, doctors at the University of Nebraska used two-way interactive television to broadcast neurologic exams across campus to medical students. Five years later, a closed-circuit television connection was built, allowing doctors to provide psychiatric consultations 112 miles away at Norfolk State Hospital.

Types
There are different types of telemedicine, including:
- Real-time video communication
- Remote monitoring, which provides for reporting, collecting, and evaluating health data, such as:
- Blood pressures
- Cardiac stats
- Oxygen levels
- Respiratory rates
- Store-and-forward, Storing and sharing medical information, such as:
- CAT scans
- MRIs
- X-rays
- Photos, videos, and text-based patient data
The convenience of telemedicine
In primary care, telemedicine usually takes the form of phone calls, where a patient consults about non-emergency medical problems that do not require a doctor’s visit. Telemedicine does not replace face-to-face consultation when needed but complements it.
The fundamental role of telemedicine now lies in the convenience it provides to patients and doctors by avoiding the need for a physical visit to receive medical advice or treatment. It is also cost-effective compared to waiting for a doctor or other healthcare provider.
Telemedicine can also help pick up urgent calls after the doctor’s office is closed. It is of excellent value in the follow-up of patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure. Those who do not experience any immediate medical problems but need help with dosage adjustments, lifestyle regimens, prescription refills, or even access to group support can benefit from the convenience of telemedicine.
An added convenience is that remote medical consultations can be arranged to follow up on all required laboratory tests or monitoring of vital signs. Doctors have practiced telemedicine for a long time, though not under that name. While this may be true, broadband Internet technology has made voice and video calling affordable and accessible to broader society, making it a viable alternative to conventional systems.

Benefits of telemedicine
Telemedicine has many benefits for people and medical professionals.
Comfort and convenience
With telemedicine, people can access care in the comfort and privacy of their own homes. This reduces the need to travel, arrange childcare and leave work. It reduces waiting time and allows people to schedule consultations around busy schedules.
Increasing access to telecare
Telemedicine helps make healthcare more accessible, especially for people living in rural areas.
Cost-effective option
Telemedicine may be more cost-effective than visiting a doctor in person and being admitted to the emergency room.
A 2020 review found that when physicians used telemedicine in the following settings, healthcare costs were reduced by 56% and travel costs by 94%.
Family support
Telemedicine allows family members and caregivers to participate in counseling, ask questions, and provide information to help care for their family members.
Prevention of chronic diseases
Telemedicine helps in providing timely preventive care to people with cardiovascular diseases. This helps prevent acute incidents and the progression of these diseases.
Controls the transmission of illnesses
Telemedicine reduces people’s exposure to others who may be sick. It also helps prevent and slow the transmission of COVID-19 and other viruses, such as the flu.
Contextualized assessments
Telemedicine allows healthcare professionals, such as occupational and physical therapists, to observe a person in their natural environment. This will enable them to make more complete assessments of a person’s abilities to move around and interact with their environment.
Disadvantages of telemedicine
Although telemedicine has many benefits, there are also disadvantages. While this field will grow exponentially over the next decade, it will bring practical and technical challenges.
Fewer face-to-face consultations
Adjusting to telemedicine is difficult for many doctors and patients, especially the elderly. While medical advances have made technology more efficient, there are times when the system breaks down. There is also the possibility of error because the technology cannot record what humans touch.
Technology is expensive
Healthcare systems adopting telemedicine solutions can attest to the time and cost involved. Implementing a new technique requires training, and sometimes employees need help to embrace the change. Although telemedicine is expensive initially, healthcare systems should have a positive return on investment over time.

Telemedicine and telehealth
The terms telemedicine and telehealth cause a lot of debate among people in the healthcare field. One of the reasons for this debate is due to the different definitions of the terms themselves. Some experts consider telemedicine physician-oriented and telehealth to include all health professionals. As medical technology advances, the two terms will likely become more distinct.
The bottom line
Today, most people have access to basic telemedicine devices such as mobile phones and computers. With better access, people in rural and congested urban areas can easily connect with a provider. Home medical devices allow caregivers to monitor everything from vitals to glucose levels. Doctors can collect essential medical information and make diagnoses without patients stepping into the doctor’s office.
Telemedicine offers a range of benefits, including convenience, savings, more contextual assessments, and involvement of family members in the individual’s care. However, it has drawbacks, including compliance and liability concerns and technical glitches. Those who want to choose this care method can ask their doctors if they offer telemedicine.
No matter where you live, you deserve the best health care possible. That’s why Dr. Arjang Naim offers telehealth services that you can access from the comfort of your own home. From contraception consultations to reviews of abnormal lab results, Dr. Arjang Naim can answer any questions you have while delivering the best care possible. Call or book an appointment online today to schedule a telehealth visit.
Additional questions
- What is another name for telemedicine?
- Telehealth
- Telemedicine
- Telecare
- What is Teleradiology in medical terms?
Teleradiology is a branch of telemedicine in which telecommunication systems transmit radiological images from one location to another. Interpretation of all non-invasive imaging studies such as digital X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine studies can be done this way.
- Is telemedicine a new technology?
Telemedicine is nothing new, although it may seem like it to many people. More than 40 years ago, technology was developed to provide diagnoses and medical care to people in remote parts of the world.
- Does telemedicine improve patient care?
Telehealth can improve the delivery of current patient education because it overcomes common barriers associated with the face-to-face model, such as time, distance, and cost.
- What are 15 medical specialties are most interested in telehealth?
- Radiology
- Psychiatry
- Internal Medicine
- Neurology
- Family Medicine
- Dermatology
- Pediatrics
- Emergency Medicine
- Geriatrics
- Allergy & Immunology
- Endocrinology
- Infectious Diseases
- Urology
- Pediatric Pulmonology
- Occupational Medicine
References
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/benefits-of-telemedicine
https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Telemedicine.aspx
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/telemedicine#summary
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/telemedicine-benefits#Best-telemedicine-for-2023
https://www.webmd.com/covid/how-does-telemedicine-work