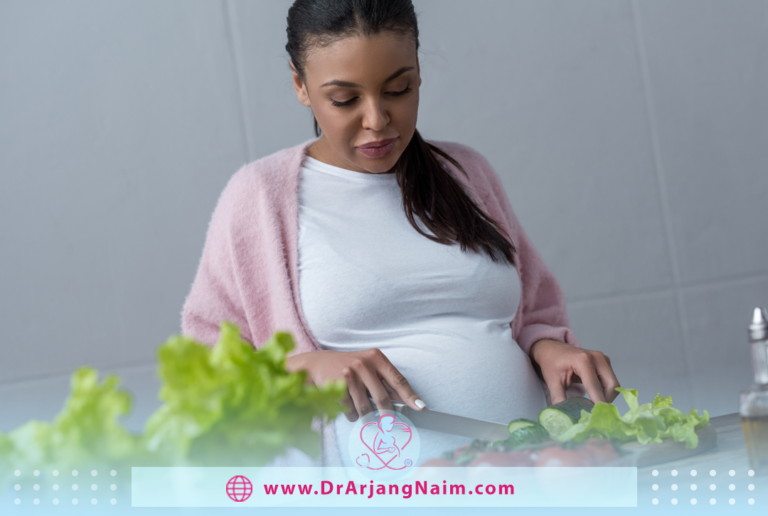
Reproductive health is one of the most important health concerns for women. Did you know that nearly 30 percent of infertility cases are linked to healthy diets, certain nutrients, and nutritional interventions or recommendations?
A balanced diet and healthy eating habits can boost fertility and improve your chances of conceiving by improving your nutritional status. Nutrients like folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants are essential in a healthy diet for both men and women. They help regulate hormones and support healthy sperm and egg production.
Eating whole foods, cutting out processed junk, and staying hydrated set the stage for better reproductive health.
The importance of nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in developing and maintaining reproductive health. A balanced diet supports reproductive function in both men and women. Essential nutrients affect hormone levels, ovulation, and sperm quality.
Women benefit from a diet rich in vitamins and minerals. For example, folate is vital before and during pregnancy. It helps prevent neural tube defects. Iron is also crucial because it supports healthy blood flow and oxygen transport.
Men also need proper nutrition for optimal fertility. Zinc is an important component in sperm production, and low zinc levels can lead to low testosterone and a reduced sperm count.
Balanced diet
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods. Vegetables and fruits have antioxidants that protect cells from damage. Whole grains have fiber and essential B vitamins that help regulate hormones.
Lean proteins are essential for tissue repair and hormone production. Sources like fish, poultry, beans, and legumes are great choices. Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, support hormone health.
Improving your diet can lead to better reproductive outcomes. Studies show that women who eat more fruits and vegetables have higher fertility rates, and men who eat a balanced diet with healthy fats produce healthier sperm.

Lifestyle factors
An active lifestyle complements a healthy diet. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, essential for reproductive health. Being overweight or underweight can disrupt hormonal balance.
Stress management is also crucial. High levels of stress can negatively impact fertility by affecting hormone levels. Practices such as meditation or yoga can help reduce stress.
Foods that may support fertility
Foods that may support fertility include a balanced diet.
Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables offer a wide range of vitamins and minerals, and it’s important to get enough nutrients before getting pregnant.
For example, foods like spinach, asparagus, broccoli, citrus fruits, nuts, legumes, whole grains, fortified breads, and cereals are rich in B vitamin folate. Folate is a natural form of folic acid, an essential nutrient in prenatal vitamins, which you should take if you’re trying to conceive.
Eating folate-rich foods during pregnancy can help prevent neural tube defects. You can lose a lot of this vitamin in the cooking water, so steam or boil vegetables in a small amount of water to preserve the folate.
In general, choose fruits and vegetables in a range of colors to get the most nutritional value.

Fish
Seafood is the best source of omega-3 fatty acids. Research shows that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is linked to an increased chance of conceiving naturally, so eating fish is safe and even recommended when trying to conceive.
On the other hand, some types of fish contain contaminants like mercury. Heavy metals in high doses harm a baby’s developing brain and nervous system. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends limiting certain fish, including albacore tuna, and avoiding swordfish, orange roughy, marlin, tilefish, king mackerel, bigeye tuna, and shark completely, as these fish have the highest levels of mercury.
The FDA also says that women trying to conceive can safely eat up to 12 ounces of fish, about two to three servings per week.
Oysters
There is scientific evidence that eating oysters can boost fertility. Oysters are packed with zinc, which plays a role in sperm and testosterone production in men and ovulation and fertility in women.
Maintaining the recommended daily zinc intake of 8 milligrams for women and 11 milligrams for men can help keep your reproductive system functioning properly. However, too much zinc can interfere with your body’s absorption of copper, negatively affecting your immune system.
Plant-based protein
Protein is an important part of a healthy diet. However, you should be careful when using plant-based protein sources alongside animal sources. Those who eat a serving of plant-based protein, such as beans, nuts, chickpeas, soy, or tofu, are less likely to experience infertility due to ovulation problems.
In addition to being lower in fat and calories than steak or chicken, including plant-based proteins in your diet can help you lose weight while boosting your fertility.
Whole grains
Eating as many nutrient-dense foods as possible while trying to conceive is recommended, and whole grains are a great option. Healthy diets that include whole grains have been linked to better fertility.
The USDA Dietary Guidelines recommend that at least half of the grains you eat daily come from whole grains, such as brown rice, oatmeal, or whole-grain bread.

Full-fat dairy products
A higher intake of full-fat dairy foods like yogurt, whole milk, and cheese was associated with a lower risk of ovulatory infertility.
Conversely, a higher intake of low-fat dairy foods such as skim milk was associated with a higher risk of ovulatory infertility.
The researchers proposed that removing the fat content from milk might alter the balance of sex hormones in a way that could negatively impact ovulation. The higher fat content in whole dairy products might positively affect these hormones. Additionally, some components found in full-fat dairy, like phosphorus and lactose, have been linked to slightly improved chances of conceiving in some studies.
Foods to avoid while trying to conceive
Certain foods should be minimized for reproductive health. It’s equally important to be aware of foods that may support fertility and those that are often recommended to be limited or avoided when trying to conceive.
High-mercury fish
As previously mentioned, fish such as sharks, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish can contain high levels of mercury, which can be harmful to a developing fetus. It’s generally recommended to limit or avoid these and choose lower-mercury options.
Processed meats
Some studies have linked high consumption of processed red meats (such as bacon, hot dogs, and salami) to reduced sperm quality in men and impaired ovulation in women. These meats can also be high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and nitrates.

Too Much caffeine
High caffeine intake has been associated with potentially reduced fertility and an increased risk of miscarriage. While moderate consumption (usually considered less than 200-300 mg per day or 1-2 cups of coffee) is often acceptable, it is wise to watch your intake from all sources (coffee, tea, soda, energy drinks, chocolate).
Alcohol
Alcohol can negatively affect fertility in both men and women. In women, it can disrupt hormone levels and menstrual cycles. In men, heavy drinking can affect sperm quality, count, and motility. Many experts recommend avoiding alcohol completely when trying to conceive to maximize your chances.
Trans fats
These unhealthy fats, often found in fried foods, processed baked goods, and margarine, have been linked to poor fertility in both men and women. They can contribute to insulin resistance and inflammation, negatively affecting ovulation and sperm health.
Sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates
They can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, potentially disrupting hormone balance and increasing the risk of weight gain, which can negatively impact fertility. Choose whole grains and limit sugary drinks, juices, and processed snacks.
Unpasteurized dairy products
These products can carry bacteria like Listeria, which can cause complications during pregnancy.
Processed foods
These foods are often high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, salt, and artificial additives while low in essential nutrients. A diet high in processed foods can negatively impact overall health and potential fertility.
The bottom line
Proper nutrition is essential for a healthy body and reproductive organs. Studies show that following a nutritious and desirable diet and making positive lifestyle changes can increase fertility and prepare the body for pregnancy. Nutrition and lifestyle choices also significantly impact the quality of sperm and eggs in the future. Healthy nutrition and lifestyle choices are essential starting today if you plan to get pregnant.
Additional questions
- What role do specific nutrients play in male fertility?
Certain nutrients are essential for male fertility. Zinc is crucial for testosterone production and sperm motility. Selenium acts as an antioxidant, protecting sperm from damage. Vitamin C also has antioxidant properties and can improve sperm quality. Folate plays a role in sperm DNA synthesis. A deficiency in these nutrients can negatively affect sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- How can nutritional deficiencies affect reproductive health in the long term?
Long-term nutritional deficiencies can have significant effects on reproductive health. For women, chronic deficiencies can lead to hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and an increased risk of conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis. In men, long-term deficiencies can lead to impaired sperm production and function, potentially leading to infertility.
- How does body weight affect fertility in men and women?
Body weight, largely determined by dietary intake and physical activity, significantly affects fertility. In women, both being underweight and being overweight can disrupt hormonal balance and ovulation, making it more difficult to get pregnant. In men, obesity can negatively affect sperm quality, sperm count, and testosterone levels.
- What is the role of antioxidants in protecting reproductive health?
Antioxidants play a vital role in protecting reproductive health by combating oxidative stress caused by free radicals. These free radicals can damage eggs, sperm, and reproductive tissues.
- How important is hydration for reproductive health?
Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, including reproductive health. Dehydration can affect the production of cervical mucus in women, which is important for sperm motility and fertilization. In men, dehydration can potentially affect semen volume and sperm concentration.
References
https://drsupriyapuranikivf.com/blog/the-impact-of-nutrition-on-reproductive-health/
https://www.inovifertility.com/blog/nutrition-and-fertility-reproductive-health/
https://www.news-medical.net/news/20230404/How-does-nutrition-affect-female-fertility.aspx
https://natural-fertility-info.com/fertility-diet