When was the last time you thought about your sperm health?
For many people, the answer to this question is never, and that’s perfectly normal. However, understanding how sperm works is important, especially when trying to conceive, as having healthy sperm is an important indicator of overall health. In simple language, sperm are the sex cells of male animals that are produced by the gonads.
What is sperm?
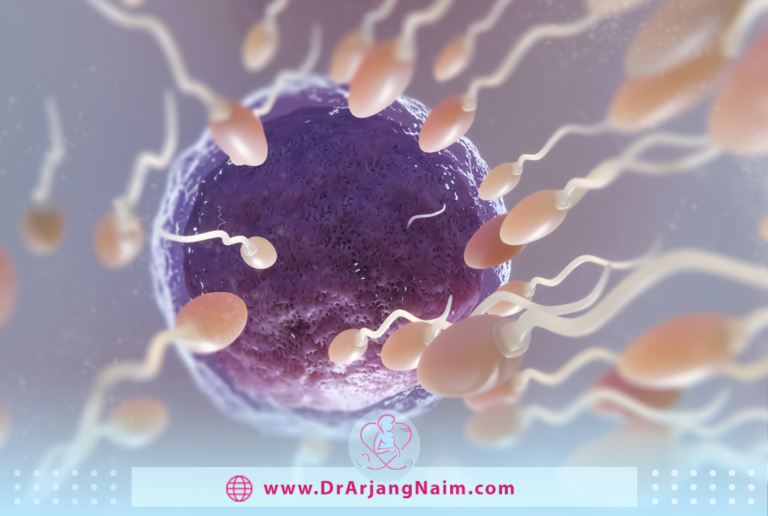
Sperm are male sex cells. You may also hear them referred to as reproductive cells or gametes. They fertilize female sex cells called eggs, which lead to pregnancy.
Parts of sperm
- Head: This part of the sperm carries 23 chromosomes, containing all the genetic information the male transmits. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell penetrates the egg and combines with the 23 chromosomes in the egg, forming a single cell of 46 chromosomes. If all goes well, the baby will be born nine months later.
- Middle: This section contains the mitochondria, which provide the sperm’s energy to move.
- Tail: Also called the flagellum, the tail propels forward through the female’s uterus and fallopian tubes in search of an egg for fertilization. The tail makes up about 90% of the length.
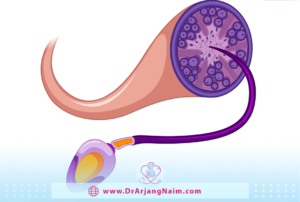
Where are sperm produced?
It is produced in two oval-shaped organs called testicles located inside the scrotum. The scrotum is a pouch of skin that hangs below the penis and helps keep the testicles cooler than the rest of the body. This cooler temperature is necessary for production.
Sperm production takes place in small tubes called spermatogenic tubes inside the testicles. Millions of sperm cells are produced daily. After production, the sperm matures in another part of the male reproductive system called the epididymis. The epididymis is a spiral tube located on top of each testicle.
What is semen?
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a whitish fluid that ejaculates from the penis during orgasm. It contains sperm cells, which are the male reproductive cells, and other fluids produced by the male reproductive organs. These fluids help to keep sperm alive and moving so that they can reach and fertilize an egg.
Here’s a breakdown of the composition of semen:
- Sperm cells: These are the male reproductive cells, making up a small percentage of the total volume of semen. Each sperm cell has a head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the genetic material (DNA) from the male, while the midpiece and tail help the sperm cell to swim.
- Seminal fluid: This is a mixture of fluids produced by several glands in the male reproductive system, including the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. Seminal fluid provides nutrients and protection for the sperm cells, and it also helps to neutralize the acidity of the vagina, which can kill sperm cells.
Semen is essential for reproduction, but it’s important to note that it’s not the same thing as sperm. Sperm cells are just one component of semen.
Where is semen formed?
Semen production is a large and very impressive production.
Semen is formed in several different places:
- Testicles: They are two small organs located inside the scrotum that produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: This long tube is located near each testicle and moves sperm from your penis to the vas deferens.
- Vas deferens: This tube connects the epididymis and the urethra, which is the hole through which urine and semen leave the body. The ductus deferens stores the sperm and removes it from the scrotum.
- Seminal vesicles: These sac-like glands are located behind the bladder and produce seminal fluid, which forms part of the seminal fluid.
- Prostate: The prostate is a gland that surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra and secretes an alkaline fluid that forms part of the semen. It also helps to ejaculate from the penis.
Once semen is made, it passes through the urethra and exits the penis during ejaculation.

How long does sperm live?
The answer depends on many things, but the most crucial factor is where the sperm are located.
On a dry surface, such as clothing or bedding, sperm are dead by the time the semen has dried. They’ll likely live longer in water, such as a warm bath or hot tub, because they thrive in warm, wet places. But the odds that sperm in a tub of water will enter a woman’s body and cause them to get pregnant are extremely low.
When sperm are inside female bodies, they can live for up to 5 days. If you’re a man or a person assigned male at birth and you have sex even a few days before your partner ovulates, there’s a chance they may get pregnant.
It’s important to remember that these are general lifespans. Several factors can influence how long sperm live inside the female body, including:
- The health: Healthier sperm with good motility (movement) will live longer than weaker sperm.
- The woman’s cervical mucus: As mentioned earlier, cervical mucus plays a key role in sperm survival.
- The presence of infections: Infections in the reproductive tract can shorten sperm lifespan.
Sperm count and motility
Sperm count refers to the number of sperm cells in a man’s ejaculate. A normal count is generally considered 15 million sperm per milliliter (ml) of semen, with a lower limit of 39 million per ml. A low sperm count can make it difficult for a man to get his partner pregnant.
Sperm count
Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm to move. Healthy sperm should be able to swim actively and in a straight line. Poor sperm motility can also reduce a man’s fertility.
There is no direct relationship between sperm count and motility, meaning a man can have a normal sperm count but poor motility or vice versa. However, both can be affected by the same factors, such as:
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can all reduce sperm count and motility.
- Medical conditions: Undescended testicles, varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum), infections, and hormonal imbalances can also affect sperm health.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to toxins, pesticides, and heavy metals can also damage sperm.

Semen analysis
If you and your partner are having trouble getting pregnant, a semen analysis is one of the first tests used to detect any problems with your male partner’s sperm.
Some things you can learn from analytics:
- Amount and thickness of semen: On average, men release 2 to 6 ml of semen with each ejaculation, which is about half a teaspoon to a teaspoon. Less than this amount may not contain enough sperm for the woman to get pregnant. On the other hand, too much can dilute the sperm concentration.
- Semen should be thick at first and thin 10-15 minutes after ejaculation. Semen that remains thick may hinder sperm movement.
Low sperm count
Many different health conditions can cause your sperm count to drop below normal. They are:
- Varicocele
- Infections
- Problems with ejaculation
One type of problem, called retrograde ejaculation, diverts semen into the bladder instead of out of the penis. The reasons for this are:
- Diabetes
- Obstruction in the tubes carrying sperm
- Spine injuries
- Surgery on the bladder, prostate, or urethra
- Cancer
- Hormonal imbalances Several hormones, including testosterone, contribute to sperm production. Problems related to any of these hormones can cause problems with sperm production.
Some medications can also interfere with sperm count by affecting the ability to produce sperm as well as the ability to ejaculate. This includes:
- Testosterone replacement therapy
- Alpha-blockers, a type of blood pressure medication
- Chemotherapy
- Some wound medications
- Some antifungal drugs and antibiotics
- Anabolic steroids
Other causes of low sperm count include:
- Exposure to industrial chemicals such as pesticides and herbicides
- Exposure to heavy metals such as lead
- Exposure to radiation or x-rays
- Smoking, alcohol and drugs
- Emotional stress and depression
- Obesity
Treatment for Low-Sperm Count Treatment depends on what is causing your low sperm count. Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Counseling, which may help with erectile dysfunction and ejaculation problems
- Hormonal treatments
- Surgery

What is sperm banking?
Sperm banking, also referred to as sperm cryopreservation or semen storage, is the process of collecting, freezing, and storing a man’s sperm for future use. It’s essentially a way to preserve a man’s fertility for later.
Why do people choose sperm banking?
Some of the most common reasons include:
- Preserving fertility before medical treatments: Certain medical treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation for cancer, can damage sperm production.
- Intentionally delaying parenthood: Some men might choose to bank sperm if they know they want to have children in the future but aren’t ready to start a family right now.
- Sperm donation: Men can also donate sperm to banks to help individuals or couples who need donor sperm to conceive.
The process of sperm banking
The process of banking is generally straightforward. Here’s a basic outline:
- Consultation
- Semen analysis
- Sample collection
- Freezing and storage
The bottom line
Sperm plays an essential role in reproduction. If you want to have a baby, you need healthy sperm. A healthy lifestyle helps keep sperm fresh.
Two key factors affecting male fertility are sperm count and motility. Those experiencing fertility problems may benefit from semen analysis. This test helps identify possible sperm problems. If you develop a problem with your sperm, there are many treatments to get them back to normal.
Additional questions
- How long does a man have sperm?
Males (people assigned male at birth) produce sperm throughout their lives unless a health condition changes their ability to do so. However, sperm count, as well as sperm health, begins to decline with age.
- What are the best ways to increase sperm count?
- Healthy lifestyle: Eat right, exercise, manage stress, and get enough sleep.
- Avoid bad habits: Smoking, excessive alcohol, tight underwear.
- Consider supplements: Vitamin C, D, and Zinc (consult a doctor first).
- See a doctor: Rule out medical conditions.
3. What kind of sperm makes a woman pregnant?
Immature sperm that are not fully formed cannot fertilize the egg. A semen sample should contain at least 50% normal and mature sperm. Semen needs a healthy concentration of sperm for optimal fertility. Fertilized semen contains at least 20 million sperm per milliliter, with a total volume of at least 2 milliliters.
- Which fruit is suitable for sperm?
Citrus fruits, such as oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, are not only refreshing but also have many fertility benefits. These fruits are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, which protect sperm cells from damage caused by free radicals and thus improve their quality and motility.
- Why is sperm watery?
If a man does not get enough zinc in his diet, he may have watery semen. Zinc is an important nutrient for sperm production. Men who ejaculate several times a day may also have watery semen, as the body needs time to build up sperm production.
References
https://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/sperm-and-semen-faq
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325906#sperm-production
https://www.healthline.com/health/healthy-sex/does-size-matter#skill
https://www.healthline.com/health/semen-vs-sperm#semens-origin