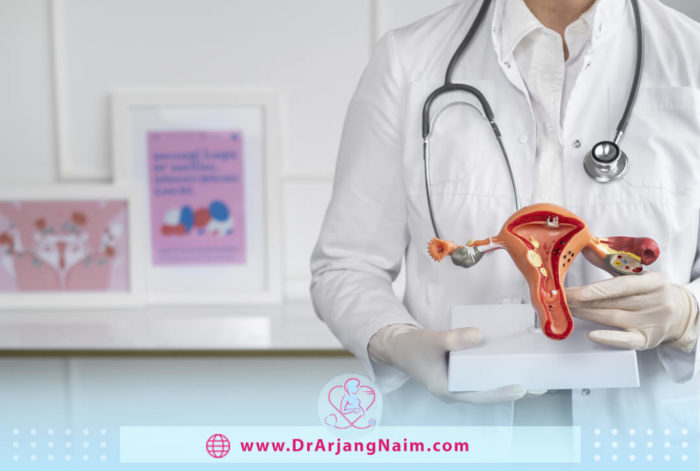
Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that normally covers the uterus (endometrial tissue) grows in the uterus’s muscle wall. The displaced tissue continues to function normally. Symptoms include heavy periods, muscle cramps, painful sex, and infertility. Doctors are not sure what causes adenomyosis, but it usually resolves after menopause. For women with severe adenomyosis, hormonal treatments can help.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this disease can be mild to severe. Even in some people, no symptoms are seen. Symptoms include:
- Blood clots during menstrual bleeding
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Painful menstrual cramps
- Infertility
Causes
The cause of adenomyosis is unknown. Possible causes include:
- Invasive tissue growth: Some experts believe that endometrial cells from the uterus lining attack the muscle that forms the uterus walls. Uterine incisions made during surgery, such as a cesarean section, may directly cause endometrial cells to invade the uterine wall.
- Developmental origins: Other experts believe that endometrial tissue builds up in the uterine muscle when the uterus first forms in the fetus.
- Uterine inflammation related to childbirth: Another theory links adenomyosis and childbirth. Inflammation of the uterus lining during the postpartum period may break the natural boundary of the cells lining the uterus.
- Stem cell origins: Bone marrow stem cells may invade the uterine muscle and cause adenomyosis.
Regardless of how adenomyosis develops, its growth depends on circulating estrogen.
Risk factors
Certain factors put people at greater risk for developing the disease. Included:
- Age: Most people are diagnosed in their 30s or 40s, a smaller proportion are diagnosed in their early teens, and some are diagnosed after the age of 50.
- Given birth before
- Undergoing treatment with the breast cancer drug
Other risk factors that have been suggested, but there is less data to support, include:
- A history of depression or antidepressant use
- Uterine surgery, such as surgery to remove uterine fibroids or cesarean delivery
- Smoking
What is the difference between adenomyosis and endometriosis?
Adenomyosis and endometriosis are disorders that affect the endometrial tissue. Both conditions can be painful. Adenomyosis is more likely to cause heavy menstrual bleeding. The difference between these conditions is where the endometrial tissue grows. Tissue growth site includes:
- Adenomyosis: Endometrial tissue grows into the muscle of the uterus.
- Endometriosis: Endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus and may involve the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and lateral walls of the pelvis.
Complications
Symptoms of adenomyosis can negatively affect lifestyle. Some people have excessive bleeding and pelvic pain that may prevent them from enjoying normal activities such as sex. People with the disease are at increased risk for anemia caused by blood loss, leading to iron deficiency. Blood loss can lower iron levels in the body. Without enough iron, the body cannot make enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues, resulting in fatigue, dizziness, and mood swings. Adenomyosis is also associated with anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic evaluation generally includes a physical examination and imaging. The doctor wants a physical and pelvic exam to determine if the uterus is enlarged or sensitive to touch. The affected people may have a uterus two or three times the normal size in some cases. Imaging tests that may be done include an ultrasound or an MRI scan.
Ultrasound
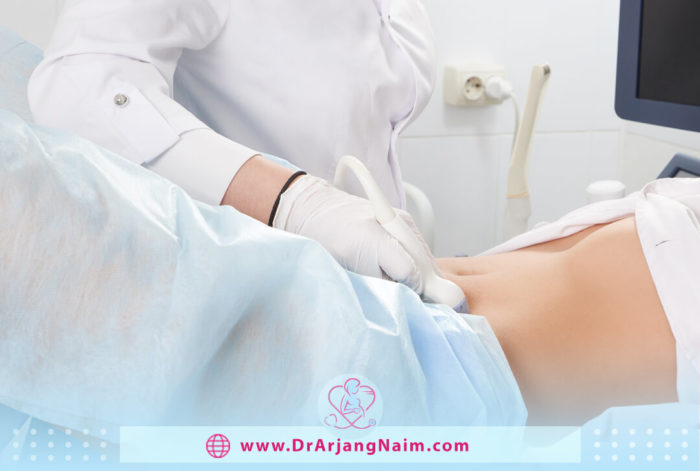
Transvaginal ultrasound can help the doctor diagnose the condition and rule out other causes. Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce moving images of the internal organs of the uterus. For this procedure, the ultrasound technician covers the ultrasound probe with a condom and then covers the condom with a liquid conductive gel. The ultrasound probe is then inserted into the body. The probe produces moving images on the screen to help the ultrasound see the anatomy of the uterus and pelvis. Ultrasound diagnosis of adenomyosis can be challenging, and the doctor may recommend more advanced imaging.
MRI scan
An imaging test of choice for the diagnosis of adenomyosis is an MRI scan. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce high-resolution images of internal organs. RI reveals the radiological features of the uterus. An example is the thickening of the area between the endometrium and the myometrium. This method involves lying motionless on a metal table that slides into the scanner. If you have an MRI, be sure to tell your doctor if you are pregnant.
How common is adenomyosis?
Many women do not know they have adenomyosis because it does not always cause symptoms. This complication may affect 20 to 65% of women.
How does adenomyosis affect pregnancy?
Adenomyosis affects women who have had at least one child. However, these conditions can make it difficult to get pregnant for the first time or have another child. Infertility treatments may help. After pregnancy, the risk of developing the following increases:
- Miscarriage
- Premature labor
Treatment
People with mild forms of adenomyosis may not need medical treatment. If symptoms interfere with daily activities or quality of life, the doctor may recommend treatment options.
Anti-inflammatory medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen can help reduce blood flow during menstruation and relieve severe cramps. The doctor will recommend that you take these medications several times. One of the possible diets includes taking anti-inflammatory drugs 2 to 3 days before the start of the period and continuing to take them during menstruation. If a woman is pregnant, she should consult a doctor before taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Hormonal treatments
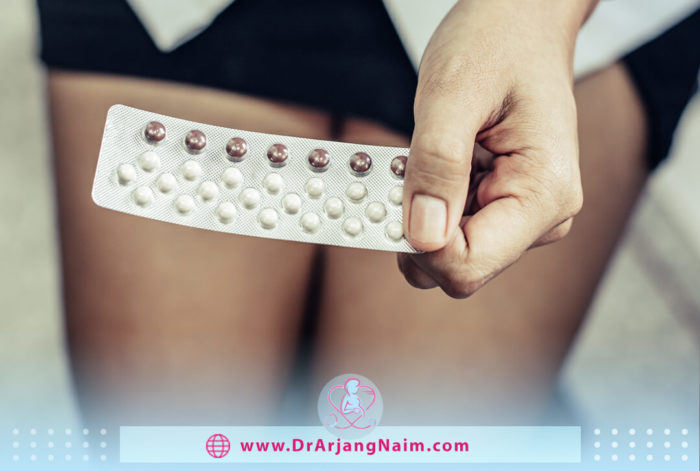

Hormone therapies can help control estrogen, which may play a role in symptoms. They are:
- Oral contraceptives such as birth control pills
- Progestin-only contraceptives
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs like leuprolide (Lupron)
Endometrial ablation
Endometrial ablation involves techniques to remove or destroy the endometrium. This is an outpatient procedure with a short recovery time. But this method may not work for everyone because adenomyosis often attacks the muscle deeper. This is only recommended for people who have finished their pregnancy or are not interested in getting pregnant.
Uterine artery embolization
Uterine artery embolization prevents the flow of certain arteries to the affected area. As blood flow stops, the adenoma shrinks. This method is commonly used to treat uterine fibroids. This procedure is performed in a hospital. Because it is minimally invasive, it does not cause scarring in the uterus.
Ultrasound – guided focused ultrasound surgery
In focused ultrasound-guided ultrasound surgery, high-intensity waves with precise focus are used to generate heat and destroy the target tissue. The heat is controlled using real-time ultrasound images.
Hysterectomy
The only way to completely cure adenomyosis is to have a hysterectomy, which involves complete removal of the uterus with surgery. It is considered a major surgical intervention used only in severe cases and in people who do not intend to give birth in the future.
When to see a doctor
A woman who is not trying to conceive or is not experiencing symptoms may not need treatment. However, any woman who suspects adenomyosis or endometriosis should see her doctor for evaluation.
If a woman is experiencing heavy periods or severe uterine cramps, it is important to discuss this with her doctor. These symptoms can be a sign of other serious illnesses, and the doctor needs to perform tests to determine the cause.
Heavy menstrual bleeding can cause anemia, which is an iron deficiency. This can make you feel tired, weak, or exhausted. Taking iron supplements can help treat anemia, which can be especially important during menstruation.
Nutrition tips for adenomyosis
Nutrients in food and the female immune system can play a major role in helping reproductive problems. There are similar dietary principles for treating endometriosis as adenomyosis, especially anti-inflammatory foods.
Consumption of vegetables

Vegetables are rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants have anti-inflammatory properties. Especially cruciferous vegetables, bell peppers, and spinach. These vegetables help balance estrogen by helping to remove estrogen.
Don’t ditch the fruit
Fruits are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. Be sure to eat two fruits a day. Berries are the fruit that is used for the peak of antioxidant power! So, eat berries at breakfast and between meals.
Sources of healthy fats
Incorporating high-quality sources of fat into the diet can improve overall pain, pain experienced during menstruation, and pain during sex. Some of the key nutrients in this category include omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E.
Vitamin E may also help reduce overall pelvic pain during menstruation and intercourse for people with endometriosis. The oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties due to its similar properties to ibuprofen. Foods to include in this group are:
- Nuts and Seeds
- Avocado
- Oily fish (sardines, trout, mackerel, salmon, anchovies)
- Extra virgin olive oil
Reduce alcohol and caffeine intake
Minimize alcohol consumption. Balance your coffee intake and avoid energy drinks, Coca-Cola, and carbonated beverages.
Reduce intake of saturated fats and excess sugar
There is a lot of research on foods high in saturated fat that contribute to the body’s pro-inflammatory response. Given that adenomyosis is an inflammatory disease, minimizing foods that trigger this type of reaction makes sense. Foods that should be kept to a minimum include:
- Coconut Oil products
- Ghee/Lard
- Processed or Fried food items
- Butter
- Cakes and pastries
Move body in a fun and enjoyable way
Find fun and enjoyable ways to move your body. Exercise is as important to mental health as it is to physical health. Having chronic pain or feeling permanently ill has a huge impact on mental health. Many people find that certain movements can improve pain symptoms, such as stretching, yoga, swimming, or light walking.
Supplements
Some vitamins, minerals, and supplements can help manage adenomyosis. A nutritionist can recommend appropriate specific supplements. Magnesium can be useful because it affects the relaxation of smooth muscles such as the uterus and gastrointestinal tract muscles. Probiotics can improve intestinal health and bowel symptoms.
The bottom line
Adenomyosis is a common disorder that affects approximately 20 to 35% of women. It causes severe menstrual pain and heavy periods, similar to endometriosis.
Adenomyosis can cause symptoms such as heavy bleeding during menstruation, menstrual cramps, pain during or after sex, and infertility. The cause is unknown, but it usually resolves after menopause. For women with severe adenomyosis, hormone therapy and hysterectomy can cure it. It can cause symptoms such as heavy bleeding during menstruation, menstrual cramps, pain during or after sex, and infertility. The cause is unknown, but it usually resolves after menopause. For women with severe adenomyosis, hormone therapy and hysterectomy can cure it.
Additional questions
1. Is adenomyosis a serious condition?
Although adenomyosis is considered a benign disease, recurrent pain, and severe bleeding can negatively impact a woman’s quality of life.
2. What is an IUD?
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped device made of plastic inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They offer long-term and reliable protection against pregnancy and are reversible. There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal.
3. Why is adenomyosis so painful?
Adenomyosis occurs when cells lining the uterus grow in the uterus’s muscle wall. As a result, the uterus becomes swollen and large, usually causing painful and heavy menstruation.
4. What vitamins help adenomyosis?
Supplements such as biotin, Diindolylmethane (DIM), and some herbal supplements regulate hormone levels. Decreased elevated estrogen levels can help reduce symptoms.
5. What is the difference between menometrorrhagia and menorrhagia?
Menometrorrhagia was an umbrella term for two different conditions, including:
- Menorrhagia: Excessive or prolonged menstruation.
- Metrorrhagia: excessive, prolonged, or irregular bleeding not associated with menstruation.
References:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adenomyosis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20369143
https://www.webmd.com/women/guide/adenomyosis-symptoms-causes-treatments
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14167-adenomyosis#management-and-treatment
https://www.healthline.com/health/adenomyosis
https://www.institutendometriose.com/en/endometriosis/what-is-adenomyosis/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321296